High blood pressure, often referred to as hypertension, is a significant health concern worldwide. Characterized by the force of blood against artery walls being too high, it can lead to severe health issues like heart disease and stroke if left unmanaged.
Understanding the causes of high blood pressure is vital for both prevention and effective management. This article delves into five primary factors contributing to this condition, offering insights into how lifestyle choices and environmental factors play a pivotal role in its development.
Causes of High Blood Pressure
1. Unhealthy Diet
High Salt Intake
One of the key dietary factors contributing to high blood pressure is high salt intake. Salt, or sodium chloride, is essential for bodily functions, but in excess, it leads to water retention.
This retention increases the volume of blood in the bloodstream, thus raising blood pressure. Processed and canned foods are often high in salt, making them major contributors to excessive sodium intake.
Fatty Foods
Foods high in saturated and trans fats can significantly impact blood pressure. These fats contribute to the buildup of plaque in the arteries (atherosclerosis), narrowing them and making it harder for the heart to pump blood efficiently.
This increased effort by the heart elevates blood pressure. Foods like fried items, certain dairy products, and some cuts of meat are rich in these unhealthy fats.
Lack of Fruits and Vegetables
A diet lacking in fruits and vegetables is another dietary risk factor for high blood pressure. Fruits and vegetables are rich in vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which are essential for maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
They also contain potassium, which helps balance the amount of sodium in the body and ease pressure on the blood vessels.
2. Lack of Physical Activity
Sedentary Lifestyle
A sedentary lifestyle is a significant risk factor for developing high blood pressure. Lack of physical activity often leads to weight gain, which is a key contributor to hypertension.
Additionally, inactivity results in weaker heart and blood vessels, exacerbating the risk of high blood pressure.
Effects on Blood Pressure
Regular physical activity is crucial in maintaining a healthy heart and vascular system. It helps in managing weight, reducing stress, and keeping the heart strong and efficient.
Exercise also helps to dilate the blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more easily, thus reducing the pressure needed to pump it through the body.
As little as 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, like brisk walking, most days of the week can significantly lower blood pressure and improve overall cardiovascular health.
3. Obesity
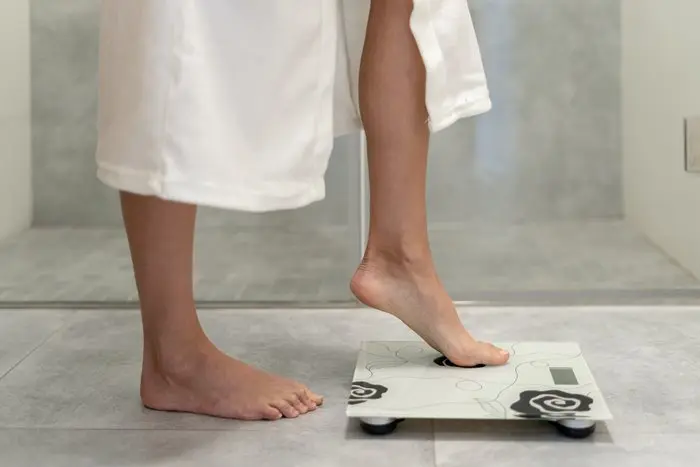

How Body Weight Affects Blood Pressure
Obesity is a significant risk factor for high blood pressure. Excess body weight means the heart must pump harder to circulate blood throughout the body, putting additional strain on the artery walls. This increased workload results in higher blood pressure.
Fat cells, particularly those around the waist (visceral fat), can also produce hormones and other substances that can further contribute to hypertension.
Visceral Fat and Risks
Visceral fat, the fat stored around the abdomen and vital organs, is particularly concerning. This type of fat is not just an inert energy store but actively produces hormones and inflammatory substances.
These substances can lead to stiffening and narrowing of the blood vessels, increasing blood pressure. Reducing visceral fat through diet and exercise is crucial in managing blood pressure effectively.
4. Alcohol and Tobacco Use
Impact of Alcohol
Regular and excessive alcohol consumption can lead to an increase in blood pressure. Alcohol contains calories, which contributes to weight gain, a risk factor for hypertension.
It can also affect the walls of the blood vessels and disrupt the balance of various bodily systems that regulate blood pressure. Moderating alcohol intake or abstaining entirely is often recommended for those with high blood pressure.
Smoking and Blood Pressure
Smoking is another major risk factor for hypertension. Nicotine, a key component in tobacco, causes the blood vessels to constrict and harden, increasing blood pressure.
Additionally, it stimulates the adrenal glands to release adrenaline, which further increases blood pressure and heart rate. Quitting smoking can significantly improve blood pressure and overall cardiovascular health.
5. Stress and Mental Health
Chronic Stress
Chronic stress is known to contribute to high blood pressure. When stressed, the body produces hormones that temporarily increase blood pressure by causing the heart to beat faster and the blood vessels to narrow.
While this is a natural response, prolonged stress without adequate relaxation and coping strategies can lead to sustained high blood pressure.
Mental Health and Hypertension
Mental health conditions like anxiety and depression can also affect blood pressure. Chronic anxiety, for example, keeps the body in a constant state of heightened alert, contributing to long-term blood pressure elevation.
Managing mental health through therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes can be an essential part of controlling blood pressure.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing the key factors of high blood pressure—unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, obesity, alcohol and tobacco use, and stress and mental health—is crucial for effective management and prevention.
By making informed lifestyle choices and seeking appropriate medical care, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of hypertension and its complications. Remember, a journey to better health always begins with small, sustainable steps towards a healthier lifestyle.